Advancing Stock Price Prediction: A Robust Framework for Noisy and Volatile Market
Integrating Signal Decomposition, Attention-Enhanced Deep Learning, and Swarm Optimization for Enhanced Accuracy
The stock market is a critical component of the global financial system, serving as a platform for capital flow, resource allocation, and economic growth. However, accurately predicting stock prices remains a persistent challenge due to the inherent complexity and uncertainty of market behavior. Stock prices are influenced by a myriad of factors, including investor sentiment, macroeconomic conditions, and sudden geopolitical events. Additionally, stock price data often exhibit nonlinearity, irregular fluctuations, and significant noise. These characteristics can obscure meaningful patterns and trends, making it difficult for predictive models to extract useful information.
Motivation
Traditional methods for stock prediction, such as statistical time series models and linear regression, often rely on simplifying assumptions about data behavior. While these models are computationally efficient, they fail to adequately capture the nonlinear interactions and high variability inherent in stock market data. Machine learning and deep learning approaches, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU), have improved predictive accuracy by modeling temporal dependencies. However, these methods are highly sensitive to noisy data, often mistaking random fluctuations for significant features. This limitation highlights the need for models that can effectively reduce noise while retaining critical information.
Objective
This study aims to develop a robust stock price prediction framework that addresses the limitations of existing models. The proposed approach combines advanced signal decomposition techniques with deep learning architectures and optimization algorithms. By decomposing stock data into simpler components, leveraging attention-based encoder-decoder frameworks, and employing intelligent parameter tuning, the model seeks to enhance predictive accuracy, especially in noisy and volatile market conditions. This integrated methodology offers a promising avenue for improving stock prediction and supporting informed decision-making in financial markets.
Proposed Methodology
Overview
The proposed framework combines signal decomposition techniques, an encoder-decoder structure enhanced by attention mechanisms, and an advanced optimization algorithm to improve stock price prediction accuracy. This integrated approach addresses the challenges posed by noisy, nonlinear data by isolating essential features, capturing temporal dependencies, and fine-tuning model parameters for optimal performance. Each component of the framework plays a critical role in enhancing predictive capabilities, especially in high-noise environments.
Signal Decomposition
To handle the complexity and noise in stock price data, the framework employs a method similar to Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN). This technique decomposes the raw stock data into intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), each representing distinct frequency components of the original signal. By breaking down the data into these components, the method isolates trends and patterns at different scales, making it easier to model relevant features while reducing noise interference.
The decomposed IMFs are categorized into high-frequency, medium-frequency, and low-frequency bands using frequency analysis. High-frequency components capture rapid fluctuations, while medium and low-frequency components reflect broader trends and stable patterns. This targeted modeling approach allows for more precise predictions by tailoring the model structure to the specific characteristics of each frequency band.
Encoder-Decoder with Attention
The framework leverages an encoder-decoder architecture for sequence prediction, which excels at capturing temporal dependencies in time series data. The encoder compresses input sequences into a latent representation, while the decoder generates predictions based on this condensed information. This structure ensures that the model retains essential features from historical data.
To further enhance feature extraction, an attention mechanism is integrated into the encoder-decoder framework. The attention mechanism dynamically assigns weights to different input elements, emphasizing the most relevant features for prediction. By focusing on key aspects of the data, the model avoids the dilution of critical information and improves its ability to capture long-term dependencies in stock price trends.
Optimization via Swarm Intelligence
An optimization strategy inspired by particle swarm optimization (PSO) is employed to fine-tune the parameters of the prediction model. This algorithm iteratively searches for the optimal combination of parameters by simulating the collective behavior of a swarm. Particles represent potential solutions, and their movement through the solution space is guided by both individual and collective learning.
To address the common challenge of premature convergence in traditional PSO, the framework incorporates modifications to the inertia weight and learning factors, enabling a balanced exploration and exploitation of the solution space. These improvements enhance the algorithm’s ability to identify global optima, ensuring that the model achieves peak predictive performance while adapting effectively to the complexities of stock price data.
The integration of these components — signal decomposition, an attention-enhanced encoder-decoder structure, and swarm-based optimization — forms a cohesive and robust framework for stock prediction in noisy and dynamic market environments.
Experimental Design
Dataset
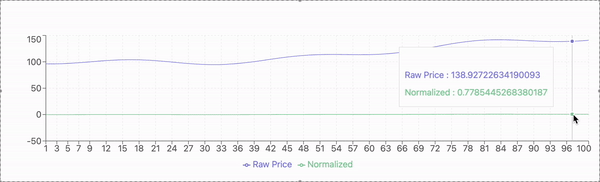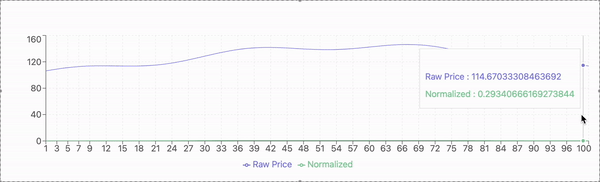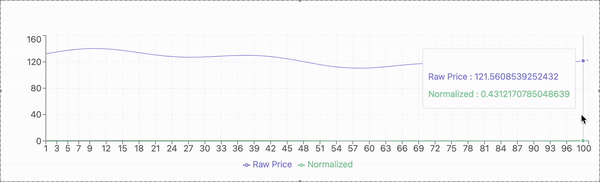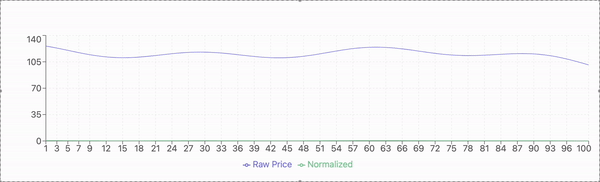
The experimental evaluation is conducted using historical stock price data from a publicly available dataset. The dataset includes daily closing prices of selected stocks over a multi-year period, capturing diverse market conditions and fluctuations. The data is preprocessed to address missing values, normalize features, and ensure compatibility with the proposed model.
For model validation, the dataset is divided into training and testing subsets. The training set comprises 80% of the data, used to train the model, while the remaining 20% serves as the testing set to evaluate predictive performance. A sliding window approach is applied, where past stock prices within a defined time frame are used to predict the next day’s closing price.
To measure the accuracy of the model, the following evaluation metrics are employed:
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): Quantifies the magnitude of prediction errors, with lower values indicating better performance.
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): Reflects the average percentage difference between predicted and actual values.
Coefficient of Determination (R²): Assesses the proportion of variance in the actual data that is explained by the model, with values closer to 1 indicating superior fit.
Comparative Studies
The proposed model is compared against several baseline models to demonstrate its effectiveness:
Single Prediction Models: LSTM and GRU, which are widely used for time series forecasting, are included to evaluate their handling of temporal dependencies in stock data.
Ensemble Models: Advanced ensemble approaches, such as hybrid neural networks combining convolutional and recurrent layers, are also considered for comparison.
The performance of each model is assessed using the same dataset, evaluation metrics, and experimental setup. The results highlight the improvements achieved by the proposed model in handling noisy data and capturing nonlinear patterns.
An ablation study is conducted to analyze the contributions of individual components in the proposed framework:
Signal Decomposition: The experiment omits the decomposition step to evaluate its role in reducing noise and enhancing model accuracy.
Attention Mechanism: The impact of removing the attention mechanism from the encoder-decoder structure is examined.
Optimization Algorithm: The model’s performance without the swarm-based optimization is compared to its fully optimized counterpart.
These ablation experiments provide insights into the importance of each component and validate the effectiveness of their integration in the proposed framework. The results demonstrate that the complete model consistently outperforms simplified versions and baseline models, establishing its robustness in predicting stock prices in dynamic market conditions.
Results and Discussion
Quantitative Results
The proposed model demonstrates superior performance in stock price prediction when evaluated against baseline models, including LSTM, GRU, and ensemble approaches. Key evaluation metrics indicate significant improvements:
Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): The model achieves a lower RMSE compared to the baselines, reflecting reduced prediction errors.
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): The MAPE is consistently lower, indicating a higher level of accuracy in percentage-based error assessment.
Coefficient of Determination (R²): The proposed model achieves an R² value close to 1, showcasing its ability to explain the variance in actual stock prices effectively.
For example, compared to LSTM, the proposed model demonstrates a marked reduction in RMSE and MAPE, alongside a substantial increase in R². Similarly, the model outperforms ensemble approaches by capturing more nuanced features and dependencies in the data.