Building StockAgent: A Comprehensive Guide to Simulating Stock Trading with Large Language Models
A Step-by-Step Guide to Building and Analyzing Realistic Financial Markets Using GPT-3.5-Turbo and Gemini-Pro
You can also download the source code using the link provided at the end.
The integration of artificial intelligence with financial markets represents one of the most significant technological advances in modern trading. At the forefront of this innovation stands StockAgent, a sophisticated multi-agent system that harnesses the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5-Turbo and Gemini-Pro to create realistic stock trading simulations. These models play a vital role in mimicking complex human decision-making processes in stock trading, offering insights into market dynamics, trader behavior, and economic trends.
The financial markets operate in highly dynamic environments where factors like market sentiment, external economic conditions, and the behavior of various stakeholders drive decision-making. Traditional models often struggle to incorporate such a diverse array of factors, but StockAgent bridges this gap by creating a rich, AI-driven simulation. By leveraging LLMs, StockAgent introduces a new level of sophistication in financial simulations, enabling users to explore not just the technicalities of trading but the psychological and emotional factors that drive market volatility.
This comprehensive guide explores the architecture, methodology, and implementation of StockAgent, offering insights into how this technology can revolutionize our understanding of market dynamics. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or financial analyst, this article will provide a blueprint for developing similar systems, empowering you to create simulations that not only reflect historical data but also account for real-time interactions and emergent market behaviors.
Project Overview
The Foundation of StockAgent
StockAgent represents a breakthrough in financial simulation technology, combining advanced LLMs with multi-agent systems to create a dynamic trading environment. Unlike traditional trading algorithms that follow preset rules, StockAgent’s agents interact in an ever-evolving market, making autonomous decisions influenced by real-time data, their interactions with other agents, and various external events like economic indicators and geopolitical trends. The agents are not limited to technical analysis but are equipped with the ability to process a wealth of data inputs, much like human traders.
The system’s primary strength lies in its ability to simulate complex market behaviors through the interaction of diverse trading agents. Each agent, powered by either GPT-3.5-Turbo or Gemini-Pro, operates with distinct personalities and trading strategies, creating a rich tapestry of market activity that closely mirrors real-world trading dynamics. For instance, one agent might favor a conservative approach, investing in stable assets, while another might take aggressive positions based on high-risk, high-reward strategies. These nuanced behaviors are what make StockAgent such a powerful tool for exploring the intricate dance of market forces.
What truly sets StockAgent apart is its ability to simulate the emergent behaviors that arise from the collective actions of multiple agents. As agents process new information from the Bulletin Board System (BBS) or react to market events, they influence one another, creating feedback loops that can lead to market rallies, crashes, or more subtle shifts in asset prices. This holistic simulation allows users to study the impact of factors like herd behavior, speculative bubbles, and market panics, which are difficult to capture using traditional models.
Core System Components
The system architecture comprises three fundamental modules that work in concert to create a realistic trading environment:
Investment Agent Module: This core component manages individual trading agents, each with unique characteristics and decision-making capabilities. Agents are designed to simulate a variety of real-world trader behaviors, from cautious long-term investors to speculative day traders. Each agent is initialized with a distinct set of resources and liabilities, ensuring that the diversity of market participants is well represented.
Transaction Module: Handles all trading activities, maintaining order books and executing trades based on complex matching algorithms. The transaction module ensures that trades are matched efficiently, respecting constraints like transaction costs, minimum order sizes, and market liquidity. It dynamically adjusts prices based on supply and demand, mimicking real-world market movements where large trades can push prices up or down.
Bulletin Board System (BBS) Module: Facilitates information exchange between agents, simulating the flow of market intelligence and trading insights. The BBS serves as a hub where agents post market predictions, share trading tips, and react to breaking news. This social aspect of the simulation reflects how real traders influence one another through media, forums, and financial networks. By analyzing BBS data, agents adjust their strategies, much like human traders react to news headlines or analyst reports.
Each of these components works in tandem to create a fully immersive market environment where agents not only trade but also influence and learn from one another. This multi-agent approach offers a realistic depiction of market dynamics, far beyond what could be achieved with traditional algorithmic trading models.
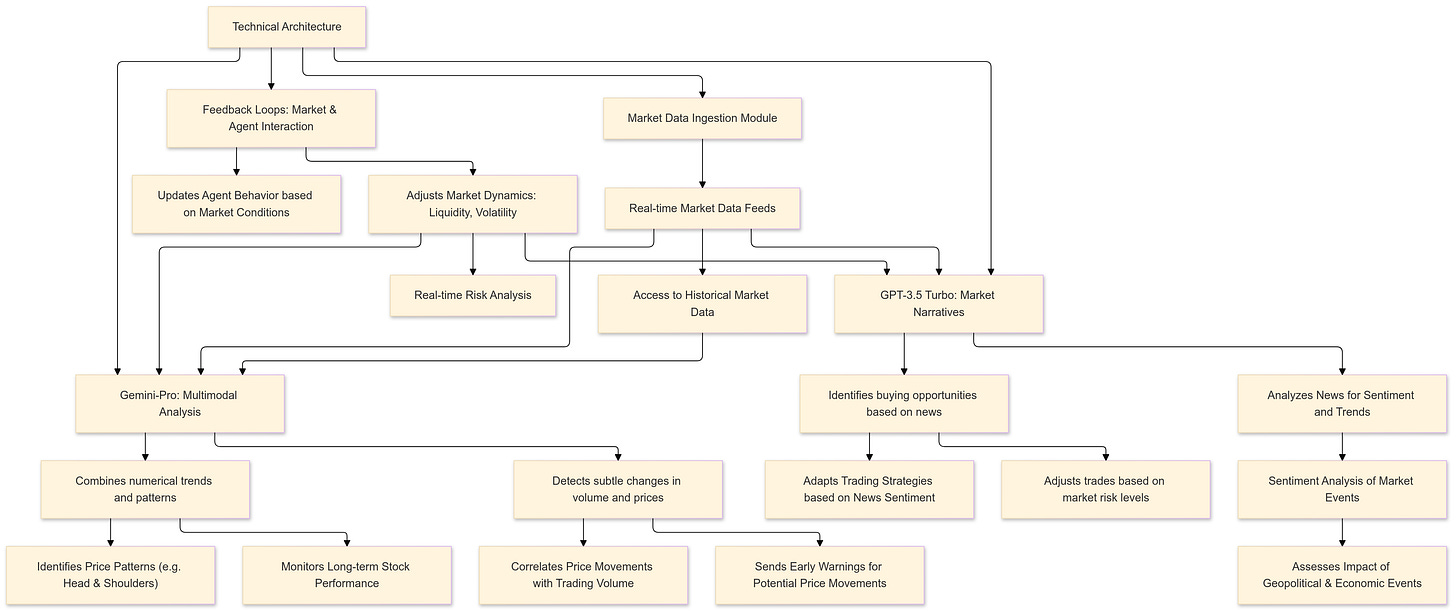
Technical Architecture
The Role of Large Language Models
StockAgent’s implementation of LLMs represents a significant advancement in trading simulation technology. Both GPT-3.5-Turbo and Gemini-Pro bring unique capabilities to the system, making the trading agents more intelligent and adaptable to changing market conditions.
GPT-3.5-Turbo
GPT-3.5-Turbo excels in processing market narratives and making nuanced trading decisions based on textual information. One of the most critical aspects of trading, especially in today’s world, is understanding market sentiment. Traders often react to news articles, analyst reports, and social media posts. GPT-3.5-Turbo allows StockAgent’s AI agents to process and interpret these narratives, making decisions that consider both quantitative data (e.g., stock prices, volume) and qualitative inputs (e.g., market sentiment, geopolitical news).
For instance, if a news article suggests a company is expected to outperform due to a new product launch, GPT-3.5-Turbo can recognize this as a bullish indicator, prompting agents to buy. Conversely, if there’s negative news about an economic downturn or regulatory hurdles, the model might suggest selling or holding off on trades. This kind of nuanced decision-making makes the trading simulation incredibly lifelike.
Gemini-Pro
Gemini-Pro adds another dimension to the simulation with its multimodal capabilities, allowing it to process various types of market data, including numerical trends and patterns, enhancing the depth of analysis available to trading agents. By combining both textual and numerical analysis, Gemini-Pro can track patterns over time, such as shifts in stock performance relative to broader market indexes, or recognize subtle signals in trading volume that suggest an impending price movement.
This multimodal ability makes Gemini-Pro particularly useful for detecting patterns that might not be immediately obvious through text alone. For example, it might detect that a stock’s price is decoupling from its fundamentals (e.g., earnings reports), suggesting a speculative bubble, and advise agents to act accordingly.
Multi-Agent System Design
The multi-agent architecture of StockAgent creates a sophisticated trading environment where each agent operates independently while influencing the broader market dynamics. This design includes multiple layers of interaction, from agent-to-agent communication to agent-environment feedback loops, all of which contribute to a dynamic and highly responsive market simulation.
Agent Initialization
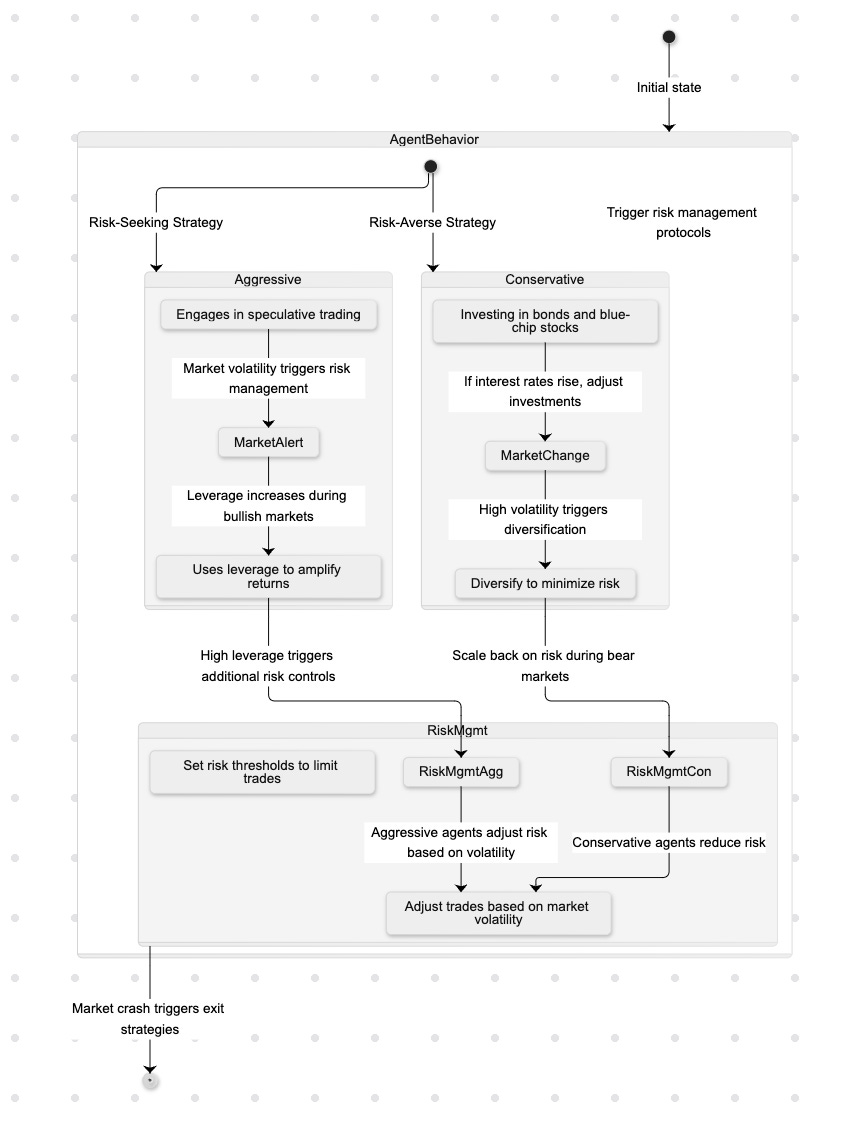
Each trading agent receives a unique combination of capital, liabilities, and personality traits. This initialization step ensures that the simulation reflects a diverse range of trading behaviors and strategies. Conservative agents might focus on low-risk investments like government bonds or blue-chip stocks, while aggressive agents might engage in speculative trading, taking on more risk in the hope of higher returns. This diversity of agent types ensures that the market behaves in a more realistic manner, as real-world markets are made up of participants with different strategies, goals, and risk tolerances.
Interaction Protocols
Agents engage in complex interactions through the Transaction and BBS modules, creating a dynamic market environment where information flow and trading activities influence collective behavior. Agents not only react to price changes but also to the information shared by other agents on the BBS. For instance, if multiple agents begin discussing an upcoming earnings report, others might anticipate increased volatility and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management
The system implements sophisticated risk assessment protocols, allowing agents to evaluate potential trades based on their risk tolerance and market conditions. These protocols help agents avoid making overly risky trades that could lead to significant losses, while still allowing for strategic risk-taking when appropriate. For instance, during a period of low market volatility, aggressive agents might increase their trading activity, whereas conservative agents might scale back their exposure to avoid unnecessary risk.
Transaction Processing
The Transaction Module serves as the heart of the trading system, managing all buy and sell orders through a sophisticated matching algorithm. It ensures that trades are executed fairly and efficiently, taking into account factors like liquidity, order size, and market impact.
Order Book Management
A robust system for tracking and matching trading orders, the order book keeps a real-time record of buy and sell offers, ensuring efficient price discovery and trade execution. Large trades can shift prices dramatically, while smaller trades are absorbed into the market with less impact. The order book reflects this dynamic, ensuring that StockAgent simulates realistic market fluctuations.
Price Discovery Mechanism
Implements dynamic price adjustments based on supply and demand, creating realistic market movements. When demand for a particular stock exceeds supply, the price rises, reflecting a real-world bidding process. Similarly, when there is an excess of sell orders, the price drops, allowing StockAgent to simulate bearish market conditions.
Trading Constraints
Enforces realistic trading rules and limitations, including transaction costs, minimum order sizes, and trading hours. These constraints ensure that the simulation mirrors real-world conditions, preventing agents from executing trades that would be impossible in actual markets (e.g., buying stocks outside of trading hours or executing trades without sufficient liquidity).
Simulation Parameters
Market Environment Setup
The simulation creates a comprehensive market environment that incorporates realistic elements from actual financial markets. This ensures that the results generated by StockAgent closely mirror those seen in real trading environments, providing valuable insights for traders and analysts alike.
Trading Calendar
A realistic trading schedule spanning 264 trading days across four quarters, allowing for the observation of seasonal patterns and long-term trends. The trading calendar includes holidays, weekends, and other periods of market closure, ensuring that the simulation operates in a realistic manner. This allows users to observe how markets behave over extended periods
, such as the “January effect” or post-earnings announcements.
Market Events
Integration of significant market events, including earnings releases, economic announcements, and regulatory changes. These events are critical to the simulation as they drive significant changes in market behavior. For example, the announcement of a new fiscal policy could cause agents to adjust their positions in response to anticipated changes in interest rates or market sentiment.
External Factors
Consideration of broader economic indicators, including interest rates, market sentiment, and global economic conditions. These external factors are often beyond the control of individual traders but have a significant impact on the market. By incorporating these elements into the simulation, StockAgent can more accurately reflect the volatility and unpredictability of real-world markets.
Agent Configuration
Trading agents within StockAgent are configured with various parameters that influence their behavior. Each agent operates under a unique set of conditions that guide their decision-making processes, from risk tolerance to investment goals.
Personality Types
Each agent is assigned one of several personality types, which guide their risk tolerance and trading strategies. These personality types include:
Conservative: Risk-averse strategies focusing on stable returns. Conservative agents are likely to invest in safe assets, such as bonds or blue-chip stocks, and avoid high-risk ventures.
Aggressive: High-risk, high-reward approaches. These agents might engage in speculative trading, seeking to capitalize on short-term price movements or volatile stocks.
Balanced: Moderate risk tolerance with diversified strategies. Balanced agents might spread their investments across a variety of asset classes, seeking a blend of stability and growth.
Growth-Oriented: Focus on long-term value appreciation. These agents prioritize investments in growth stocks or emerging markets, accepting short-term volatility in exchange for potential long-term gains.
Financial Parameters
Initial capital ranging from 100,000 to 5,000,000 currency units: Each agent starts with a different level of resources, reflecting the diversity of real-world traders, from retail investors to institutional players.
Various debt levels and credit accessibility: Some agents may take on loans to finance their trades, introducing another layer of complexity and risk.
Different transaction cost structures: Transaction costs are an essential consideration in trading, and StockAgent simulates different cost structures, from flat fees to percentage-based commissions.
Market Conditions
The simulation incorporates realistic market conditions that affect how agents trade and make decisions. These conditions are dynamic, changing over time based on the simulated economic environment.
Interest Rate Environment
Implementation of varying interest rates affecting borrowing costs and investment decisions. During periods of low interest rates, agents may be more inclined to borrow money for investment, leading to increased market activity. Conversely, high-interest rates might suppress trading as the cost of borrowing rises.
Liquidity Conditions
Dynamic liquidity levels that influence trading costs and execution capabilities. In a liquid market, agents can execute large trades without significantly impacting the price. However, in a less liquid environment, even small trades can cause sharp price movements, reflecting the challenges of trading in thinly traded assets.
Market Sentiment
Integration of changing market sentiment that affects trading behavior and price movements. Market sentiment can be driven by news, social media, and broader economic conditions, influencing whether agents are bullish or bearish on particular assets. By incorporating sentiment analysis, StockAgent can simulate the emotional and psychological factors that drive real-world markets.
Experimental Design
Test Scenarios
StockAgent implements various test scenarios to evaluate system performance, enabling users to observe how agents behave under different conditions and how the system responds to various market dynamics.
Basic Testing
Initial 10-day simulations to verify system functionality and basic agent interactions. These short-term tests allow developers to fine-tune the system, ensuring that agents are making rational decisions and that the simulation is running smoothly.
Extended Testing
Comprehensive 154-day simulations to observe long-term patterns and system stability. These tests are crucial for evaluating how agents respond to sustained market trends and whether the system can maintain performance over longer periods.
Stress Testing
Evaluation of system performance under extreme market conditions and high trading volumes. Stress testing simulates market crashes, liquidity crises, or surges in trading activity, allowing developers to identify potential bottlenecks or vulnerabilities in the system.
Performance Metrics
The system tracks multiple performance indicators, providing a detailed picture of both individual agent performance and overall market conditions.
Trading Metrics
Transaction volumes and frequencies: These metrics track how often agents are trading and how much volume they are moving. High trading volumes might indicate a speculative frenzy, while low volumes could suggest a lack of market confidence.
Price movement patterns: By analyzing how prices change over time, the system can identify trends, such as momentum-driven price movements or mean-reverting behavior.
Order execution rates: The system tracks how many orders are successfully executed and how many remain unfulfilled, providing insights into market liquidity and efficiency.
Market liquidity levels: Liquidity is a critical factor in trading, and StockAgent tracks how easily agents can buy and sell assets without affecting prices.
Agent Performance
Profit and loss statistics: Each agent’s profitability is tracked over time, allowing for a comparison of different strategies and risk tolerances.
Risk-adjusted returns: This metric considers not just the raw returns but the amount of risk taken to achieve them. Agents that achieve high returns with low risk are considered more efficient.
Trading strategy effectiveness: By comparing the performance of different strategies, the system can determine which approaches are most effective under various market conditions.
Portfolio composition changes: The system tracks how agents adjust their portfolios over time, providing insights into their long-term investment strategies.
System Performance
Processing efficiency: The system tracks how quickly it can process transactions and update market conditions, ensuring that it can handle high volumes of data and trades.
Order matching accuracy: Ensures that trades are executed correctly and fairly, maintaining the integrity of the simulation.
Information dissemination effectiveness: Measures how quickly and accurately information is shared among agents, ensuring that all participants have access to the same data.
System stability under load: Stress testing ensures that the system remains stable even under high volumes of trades or extreme market conditions.
Results Analysis
Comparative Analysis
StockAgent enables detailed comparison of different trading strategies and market conditions, providing valuable insights into how various factors influence agent behavior and market outcomes.
Agent Performance
The system allows for a granular analysis of how different personality types perform under various market conditions. For example, conservative agents might outperform during bear markets, while aggressive agents might excel during bull runs. By comparing the performance of different agent types, users can gain insights into the effectiveness of various trading strategies.
Model Comparison
Evaluation of trading decisions made by GPT-3.5-Turbo versus Gemini-Pro agents provides insights into how different LLMs influence trading behavior. GPT-3.5-Turbo might excel in interpreting market sentiment and reacting to news, while Gemini-Pro could be more effective at identifying long-term trends through numerical analysis. This comparison helps users understand the strengths and weaknesses of each model in different market environments.
Strategy Effectiveness
StockAgent assesses the effectiveness of various trading strategies across different market cycles. For instance, momentum-based strategies might work well in trending markets but underperform in range-bound markets. By simulating different market conditions, StockAgent helps users identify which strategies are most robust.
Market Impact Analysis
The system provides insights into how different factors affect market behavior, offering a detailed picture of how agents influence prices and liquidity.
Price Impact
StockAgent evaluates how trading decisions influence price movements and market stability. For example, large trades by aggressive agents might cause significant price fluctuations, while smaller, more frequent trades by conservative agents might stabilize the market. This analysis helps users understand the relationship between trade size and market impact.
Information Flow
The system analyzes how information dissemination through the BBS affects trading decisions. When agents share insights on the BBS, other agents might adjust their strategies in response, leading to feedback loops that can amplify certain market trends. By studying this information flow, users can gain insights into how rumors, news, and analyst reports influence market behavior.
Market Efficiency
StockAgent assesses price discovery and market liquidity under different conditions. Efficient markets are characterized by quick price adjustments in response to new information, while inefficient markets might experience delayed reactions or mispricings. By simulating various levels of market efficiency, StockAgent helps users identify factors that contribute to more stable and liquid markets.
Implementation Considerations
Technical Requirements
Successful implementation of StockAgent requires careful consideration of the technical infrastructure needed to support a complex multi-agent system.
Computing Infrastructure
Adequate processing power and memory are essential to handle multiple concurrent agents and transactions. Depending on the scale of the simulation, developers may need to deploy StockAgent on cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud, where they can take advantage of scalable computing resources.
Data Management
Efficient storage and retrieval systems are required to manage the vast amounts of data generated by the simulation. This includes market data, transaction logs, agent behavior records, and BBS messages. Using databases like PostgreSQL or MongoDB can help ensure that data is stored efficiently and can be accessed quickly.
Network Capacity
Robust networking capabilities are necessary to handle real-time information flow and trade execution. In a distributed system where agents may be running on different servers, network latency can affect how quickly agents receive information and make decisions. Ensuring that the system has sufficient bandwidth and low-latency connections is critical for maintaining the realism and accuracy of the simulation.
Operational Considerations
In addition to technical requirements, there are several operational factors that developers must consider when implementing StockAgent.
System Monitoring
Continuous oversight of system performance and trading activities is essential to ensure that the simulation is running smoothly. Monitoring tools like Grafana or Prometheus can help developers track key performance metrics, identify potential bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Risk Controls
To prevent agents from engaging in reckless trading, the system must implement robust risk controls. This might include setting maximum leverage
limits, imposing transaction fees, or implementing circuit breakers that halt trading during periods of extreme volatility. These controls ensure that the simulation remains realistic and that agents are not able to exploit loopholes in the system.
Data Backup
Regular backup of system state and trading records is essential to prevent data loss in the event of a system failure. Automated backup solutions can ensure that the system’s data is regularly saved and can be restored in case of an emergency.
Future Developments
Potential Enhancements
Several areas for future development have been identified, which could further enhance the functionality and capabilities of StockAgent.
Advanced Analytics
Integration of more sophisticated market analysis tools, such as predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms, could provide agents with more advanced decision-making capabilities. For example, agents could use machine learning models to predict future market movements based on historical data or identify correlations between different asset classes.
Improved Agent Intelligence
Enhancement of agent decision-making processes through more advanced AI models could lead to even more realistic trading behavior. By incorporating reinforcement learning techniques, agents could learn from their past trades and adjust their strategies over time, leading to more adaptive and resilient trading agents.
Market Coverage
Expansion to additional asset classes and market types could make StockAgent more versatile. In addition to equities, the system could be expanded to simulate bond markets, commodities, or even cryptocurrency markets. This would allow users to study a broader range of financial markets and trading strategies.
Research Opportunities
StockAgent opens up numerous research possibilities, particularly in the areas of market behavior and AI-driven trading strategies.
Market Behavior
Deep analysis of how different factors, such as liquidity, market sentiment, and external events, influence market dynamics could provide valuable insights into the functioning of financial markets. Researchers could use StockAgent to study the causes of market bubbles, crashes, or other anomalies.
AI Trading Strategies
Development and testing of new AI-driven trading approaches could lead to the discovery of novel strategies that outperform traditional methods. Researchers could experiment with different AI models, such as neural networks or decision trees, to determine which approaches are most effective in various market conditions.
Risk Management
Investigation of novel risk assessment and management techniques could lead to the development of more robust risk controls. Researchers could use StockAgent to study the effectiveness of different risk management strategies, such as diversification or hedging, and determine which techniques are most effective in mitigating losses.
Conclusion
StockAgent represents a significant advancement in the field of market simulation and trading system development. Its sophisticated architecture and use of cutting-edge LLMs provide valuable insights into market dynamics and trading behavior. The system’s ability to simulate complex market interactions while maintaining realistic trading conditions makes it an invaluable tool for research, training, and strategy development.
The success of StockAgent demonstrates the potential for AI-driven systems to enhance our understanding of financial markets and improve trading strategies. By simulating the behavior of diverse market participants and incorporating external factors, StockAgent offers a more holistic view of market dynamics than traditional models. As technology continues to evolve, systems like StockAgent will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of financial markets and trading practices.
Recommendations
For organizations and researchers interested in implementing similar systems, the following recommendations are provided:
Development Approach
Start with simplified models and gradually increase complexity: Begin by building a basic multi-agent system and then incrementally add features such as LLMs, external events, and complex trading strategies.
Focus on robust testing and validation procedures: Ensure that the system is thoroughly tested under various market conditions to identify potential issues and optimize performance.
Maintain detailed documentation of system behavior and performance: Comprehensive documentation will make it easier to troubleshoot issues, refine the system, and onboard new users.
Implementation Strategy
Ensure adequate computing resources are available: StockAgent’s multi-agent system requires significant processing power, particularly for large-scale simulations or stress testing scenarios.
Develop comprehensive monitoring and control systems: Real-time monitoring of agent behavior, system performance, and market conditions is essential for maintaining the integrity of the simulation.
Plan for scalability and future enhancements: As the system evolves, it will need to accommodate additional agents, asset classes, and market conditions. Building a flexible, scalable architecture will ensure that StockAgent can grow alongside the needs of its users.