Harnessing Sentiment: Predicting Stock Movements in the Pharmaceutical Sector
An Analysis of News Sentiment’s Impact on Financial Forecasting and Investment Strategies
You can now listen to the article, if not wanting to read.
Download the source code from the link at the end of this article.
In the dynamic realm of global finance, the ability to accurately forecast stock market movements stands as a cornerstone for strategic investment and effective business planning. The stock market, often perceived as a barometer of economic health, plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial trajectories of businesses and the investment decisions of individuals and institutions alike. As markets become increasingly complex and influenced by a multitude of factors, the quest for reliable prediction models has intensified, driving innovation across various academic and professional disciplines.
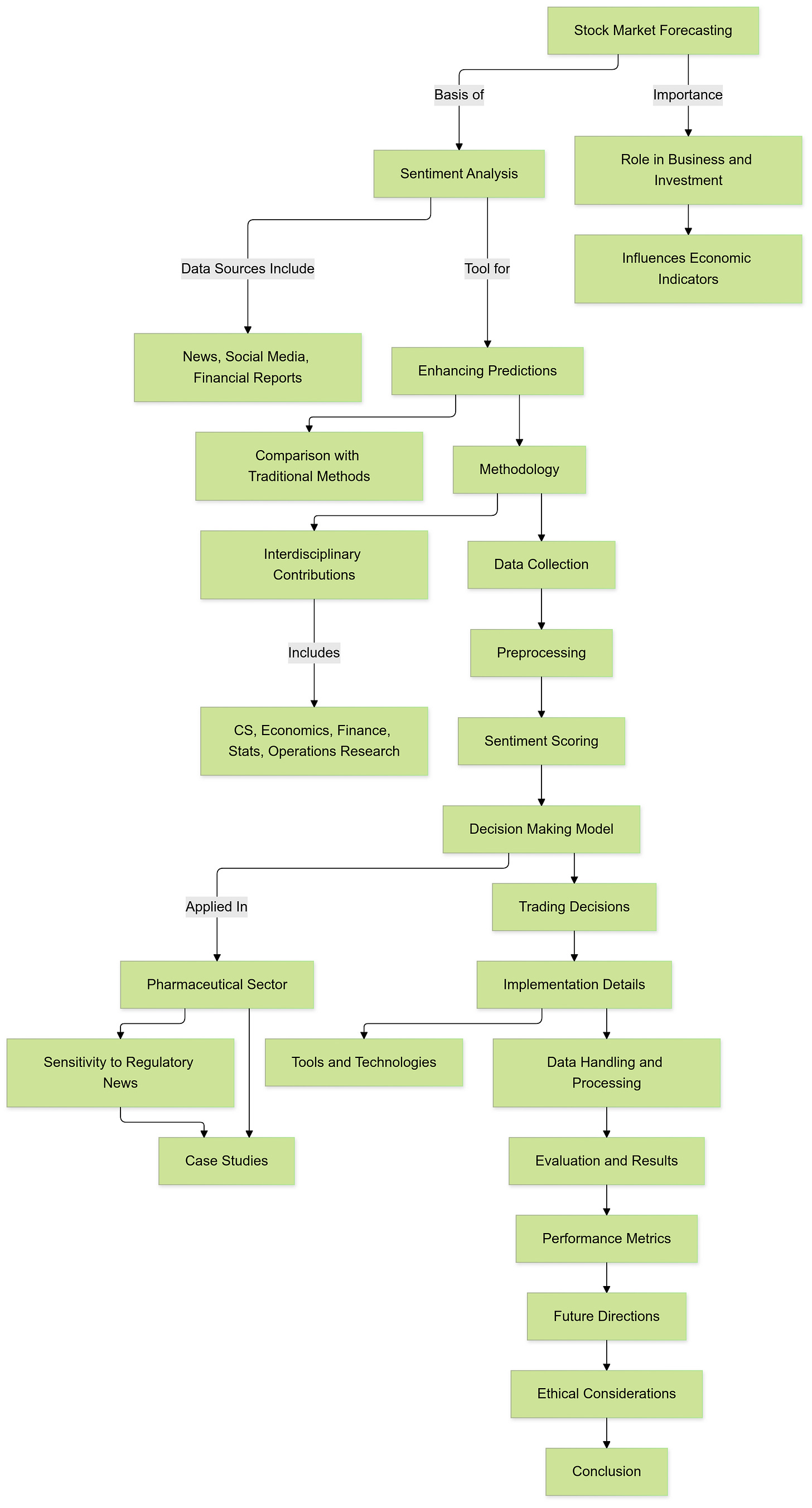
Importance of Stock Market Forecasting
Stock market forecasting is essential for several reasons. For businesses, understanding market trends allows for informed decision-making regarding capital investments, expansion plans, and risk management. Accurate predictions can help companies anticipate market fluctuations, optimize their financial strategies, and maintain competitive advantage. For investors, whether individual or institutional, forecasting provides a foundation for portfolio management, enabling the identification of lucrative investment opportunities and the mitigation of potential losses. Moreover, policymakers and economists rely on stock market trends to gauge economic stability, inform regulatory decisions, and implement measures that foster sustainable growth.
The significance of stock market movements extends beyond individual entities, impacting broader economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and consumer confidence. Consequently, the ability to predict stock price fluctuations with high accuracy is not only beneficial for immediate financial gains but also for fostering long-term economic resilience and prosperity.
Relevance of Sentiment Analysis in Modern Financial Markets
In recent years, sentiment analysis has emerged as a transformative tool in the arsenal of financial forecasting. Sentiment analysis, a branch of Natural Language Processing (NLP), involves the computational identification and categorization of subjective information — such as opinions, emotions, and attitudes — within textual data. Its relevance in financial markets is underscored by the increasing availability and accessibility of vast amounts of unstructured data from diverse sources, including news articles, social media platforms, and financial reports.
The financial markets are inherently influenced by the collective sentiment of investors and the general public. News headlines, analyst reports, and even casual social media posts can sway investor behavior, leading to significant market movements. Traditional forecasting models, which predominantly rely on quantitative data such as historical prices and trading volumes, often overlook the qualitative aspects of market sentiment. By integrating sentiment analysis into predictive models, analysts can capture the nuanced sentiments that drive market psychology, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of their forecasts.
Stock Market Significance
The stock market serves as a vital mechanism for the allocation of capital, enabling businesses to raise funds for growth and expansion while providing investors with opportunities to earn returns on their investments. Movements in stock prices reflect a myriad of factors, including company performance, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. For businesses, understanding these movements is crucial for strategic planning and operational efficiency. For instance, a sustained rise in stock prices may signal investor confidence, encouraging companies to embark on new projects or increase production capacity. Conversely, declining stock prices may prompt businesses to reassess their strategies, cut costs, or seek alternative financing options.
For investors, the stock market offers a platform for wealth accumulation and diversification. Accurate forecasting empowers investors to make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling stocks, optimizing their investment portfolios to achieve desired financial outcomes. Additionally, institutional investors, such as mutual funds and pension funds, rely on market forecasts to manage large-scale investments and ensure the financial security of their beneficiaries.
Interdisciplinary Interest
The pursuit of accurate stock market forecasting is inherently interdisciplinary, bridging the realms of computer science, economics, finance, statistics, and operations research. Each discipline contributes unique methodologies and perspectives that collectively enhance the robustness of predictive models.
Computer Science and Machine Learning: Advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence have revolutionized data analysis, enabling the processing of vast datasets with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Techniques such as neural networks, support vector machines, and ensemble methods are employed to identify complex patterns and correlations within financial data.
Economics and Finance: These disciplines provide the theoretical frameworks and quantitative models that underpin financial analysis. Concepts such as market efficiency, behavioral finance, and econometric modeling are integral to understanding and predicting market dynamics.
Statistics and Data Science: Statistical methods are essential for data preprocessing, hypothesis testing, and the evaluation of model performance. Data science techniques facilitate the extraction of meaningful insights from heterogeneous data sources, enhancing the predictive power of financial models.
Operations Research: This field contributes optimization techniques and decision-making frameworks that are crucial for developing effective trading strategies and portfolio management systems.
The convergence of these disciplines fosters a holistic approach to stock market forecasting, leveraging computational power and theoretical rigor to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
Role of Public Sentiment
Public sentiment plays a critical role in shaping investor behavior and, consequently, market trends. The sentiment expressed in news articles, social media posts, and financial reports can influence perceptions of a company’s prospects, leading to fluctuations in stock prices. Positive sentiment may engender investor confidence, driving up stock prices, while negative sentiment can trigger fear and uncertainty, resulting in stock sell-offs.
The advent of digital media has amplified the impact of public sentiment on financial markets. Real-time dissemination of information through online platforms allows sentiment to spread rapidly, often preceding traditional market indicators. For instance, a viral tweet from a prominent financial influencer or a breaking news story about a regulatory approval can cause immediate and significant movements in stock prices. By capturing and analyzing this sentiment, investors and analysts can gain a competitive edge in anticipating market reactions.
Moreover, sentiment analysis enables the detection of subtle shifts in market mood that may not be immediately apparent through quantitative data alone. For example, an increase in negative sentiment surrounding a company’s product recalls or regulatory challenges can signal potential declines in stock performance, prompting preemptive trading actions.
Focus on Pharmaceutical Sector
The pharmaceutical sector presents a particularly compelling case for the application of sentiment analysis in stock market forecasting. This industry’s sensitivity to regulatory news, clinical trial outcomes, and global health events makes it highly responsive to public sentiment and media coverage. Regulatory decisions from bodies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can significantly influence a pharmaceutical company’s stock performance. Positive drug approvals can lead to substantial revenue growth and investor optimism, while negative outcomes, such as failed trials or safety concerns, can result in sharp declines.
Additionally, the global nature of the pharmaceutical industry means that news from various regions can impact stock prices. International collaborations, patent disputes, and geopolitical events can all contribute to the volatility of pharmaceutical stocks. By focusing on this sector, the study leverages the pronounced effects of news sentiment on stock movements, providing a clear and measurable relationship between sentiment indicators and market performance.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical sector’s reliance on innovation and research underscores the importance of staying attuned to public and investor sentiment. Companies that effectively communicate their research advancements and navigate regulatory landscapes can foster positive sentiment, enhancing their market valuation. Conversely, missteps in communication or adverse regulatory outcomes can erode investor confidence, highlighting the critical role of sentiment analysis in managing financial risk and seizing investment opportunities.
Methodology
The methodology employed in this study is meticulously designed to analyze news sentiment and predict stock movements within the pharmaceutical sector. This comprehensive approach integrates data collection, preprocessing, sentiment analysis, and decision-making models to ensure robust and accurate predictions. The following sections elucidate each component of the methodology in detail.
Data Collection
Effective data collection forms the backbone of any predictive analysis. In this study, both news articles and stock price data are systematically gathered to facilitate the sentiment-driven prediction model.
News Articles
Source Selection:
To ensure the reliability and relevance of the data, reputable financial news platforms specifically catering to the pharmaceutical sector are selected as primary sources. These platforms provide timely and accurate information crucial for understanding market sentiment. Examples of such sources include major financial news websites, industry-specific publications, and authoritative press release distributions. The chosen platforms are recognized for their comprehensive coverage of regulatory updates, corporate announcements, and market analyses pertinent to pharmaceutical companies.
Time Frame:
The period for data collection is defined as the past six months. This time frame is strategically chosen to capture recent trends and sentiments that can influence short-term stock movements. A six-month span offers a balance between having sufficient data points for analysis and maintaining relevance to current market conditions.
Filtering Criteria:
To curate a dataset that is highly relevant to the pharmaceutical sector, specific keywords related to regulatory bodies and financial performance indicators are employed. Keywords such as “FDA” (Food and Drug Administration), “EMA” (European Medicines Agency), “Q1” (first quarter), “Q2” (second quarter), “clinical trial,” and “drug approval” are used to filter news articles. These terms are indicative of significant events and developments that can materially impact stock prices. Additionally, articles mentioning mergers, acquisitions, patent filings, and safety recalls are included to encompass a broad spectrum of factors influencing investor sentiment.
Stock Price Data
Source Selection:
Reliable financial data providers are utilized to obtain both intraday and historical stock price information. Platforms such as Bloomberg, Reuters, and Investing.com are selected for their accuracy, comprehensiveness, and real-time data provision capabilities. These sources offer extensive datasets that include not only stock prices but also trading volumes, market indices, and other financial metrics essential for thorough analysis.
Granularity:
Stock price data is collected at 30-minute intervals. This granularity is chosen to capture the nuanced movements of stock prices in response to news releases and sentiment shifts. Half-hourly data points provide a detailed temporal resolution, enabling the identification of immediate market reactions following news events. This level of detail is crucial for short-term prediction models that rely on timely data to inform trading decisions.
Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is a critical step that ensures the quality and consistency of the data, laying the foundation for accurate sentiment analysis and prediction.
Cleaning
Text Cleaning:
The raw text from news articles often contains various artifacts that can hinder analysis. To prepare the data for sentiment analysis, the following cleaning steps are undertaken:
Punctuation Removal: All punctuation marks are stripped from the text to focus solely on the words.
Special Characters: Any special characters, including symbols and emojis, are removed to eliminate noise.
Whitespace Handling: Excessive whitespace is trimmed to maintain uniformity across the dataset.
Case Normalization: All text is converted to lowercase to ensure consistency in word matching during analysis.
Deduplication:
Duplicate news articles can skew sentiment analysis by overrepresenting certain sentiments. To maintain data quality, duplicate articles are identified and removed. This ensures that each news piece contributes uniquely to the sentiment scoring, providing an unbiased basis for predicting stock movements.
Tokenization
Process:
Tokenization involves breaking down the cleaned text into smaller units — words or phrases — that can be analyzed for sentiment. This process transforms unstructured text into a structured format suitable for computational analysis.
N-grams Generation:
To capture the context and nuanced meanings within the text, n-grams are generated. This includes:
Unigrams: Single-word tokens that serve as the basic building blocks for sentiment analysis.
Bigrams: Two-word combinations that help in understanding the relationship between adjacent words (e.g., “price increase”).
Trigrams: Three-word sequences that provide deeper context and capture more complex sentiment expressions (e.g., “regulatory approval success”).
Stemming:
Stemming is applied to reduce words to their base or root forms. For instance, words like “approving,” “approved,” and “approves” are reduced to “approve.” This standardization facilitates more accurate matching of words against the sentiment dictionary, ensuring that different morphological forms of a word are treated uniformly.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is the core component of this methodology, translating textual data into quantifiable sentiment scores that inform stock prediction models.
Dictionary-Based Approach
Dictionary Creation:
A specialized sentiment dictionary is developed specifically for the pharmaceutical sector. This dictionary comprises 100 carefully selected words and phrases that are indicative of positive, negative, or neutral sentiments within the context of pharmaceutical news. The creation process involves:
Domain Expertise: Leveraging insights from industry experts to identify terms that have significant implications for stock performance.
Literature Review: Analyzing past news articles and their impact on stock prices to identify recurring sentiment-bearing terms.
Categorization: Each term is classified into one of three categories — positive, negative, or neutral — based on its typical impact on investor sentiment and stock movements.
Comparison Process:
The generated n-grams from the tokenized news articles are systematically compared against the sentiment dictionary. Each n-gram that matches an entry in the dictionary is assigned a corresponding polarity score:
Positive Terms: Assigned positive values indicating favorable sentiment.
Negative Terms: Assigned negative values indicating adverse sentiment.
Neutral Terms: Do not contribute to the sentiment score, serving as neutral indicators.
Scoring Mechanism:
For each news article, the sentiment scores are aggregated by tallying the frequency of positive and negative terms. The overall sentiment score for an article is calculated as the difference between the total positive and negative scores. This aggregate score serves as a quantitative measure of the sentiment conveyed in the news piece:
Positive Score: Indicates a bullish sentiment, potentially signaling a price increase.
Negative Score: Indicates a bearish sentiment, potentially signaling a price decrease.
Neutral Score: Suggests a lack of significant sentiment, indicating minimal impact on stock price.
Decision-Making Model
The decision-making model translates sentiment scores into actionable trading decisions, forming the basis for the stock prediction strategy.
Strategy Development
Buy/Sell/Hold Decisions:
Based on the aggregated sentiment scores, predefined rules are established to determine whether to buy, sell, or hold a stock. The decision rules are as follows:
Buy: If the sentiment score is positive and exceeds a certain threshold, indicating strong positive sentiment that is likely to drive the stock price upwards.
Sell: If the sentiment score is negative and falls below a certain threshold, indicating strong negative sentiment that is likely to drive the stock price downwards.
Hold: If the sentiment score is neutral or does not meet the buy/sell thresholds, suggesting that the stock price is unlikely to experience significant movement.
Thresholds:
Specific percentage thresholds are defined to quantify the sentiment scores and guide decision-making:
0.5% Threshold for Buy/Sell: A sentiment score above +0.5% triggers a buy decision, while a score below -0.5% triggers a sell decision. These thresholds are calibrated to reflect meaningful sentiment shifts that are expected to result in noticeable stock price movements.
1% Threshold for Hold: A sentiment score within the range of -0.5% to +0.5% suggests minimal sentiment influence, prompting a hold decision. This higher threshold accounts for the possibility of minor fluctuations that do not warrant immediate trading actions.
Portfolio Simulation
Trading Execution:
To evaluate the efficacy of the sentiment-based decision model, a portfolio simulation is conducted. The simulation assumes that trades (buy or sell) are executed within thirty minutes of the news release. This short time frame is chosen to capture immediate market reactions to news sentiment before other factors can influence the stock price significantly.
Return Calculation:
The performance of the trading strategy is measured by calculating the returns based on the difference between the trade execution price and the closing price of the day. Specifically:
Buy Decision: The return is calculated as the difference between the closing price and the buy price. A positive return indicates a profitable trade, while a negative return indicates a loss.
Sell Decision: The return is calculated as the difference between the sell price and the closing price. A positive return indicates a profitable trade from selling at a higher price, while a negative return indicates a loss from selling at a lower price.
Hold Decision: No trading action is taken, and thus no return is realized from the hold decision.
Threshold Implementation:
The predefined thresholds ensure that only significant sentiment changes lead to trading actions, thereby reducing the impact of noise and minor sentiment fluctuations. For example, if the sentiment score for a news article about a pharmaceutical company exceeds +0.5%, the model suggests buying the stock, anticipating a price increase. Conversely, a sentiment score below -0.5% suggests selling the stock in anticipation of a price decrease. If the sentiment score does not meet these thresholds, the model advises holding the stock, indicating stability or minimal expected movement.
Implementation Details
While not explicitly outlined in the initial blueprint, it is crucial to detail the implementation process to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the methodology is executed in practice.
Programming Environment:
The study leverages Python as the primary programming language due to its extensive libraries and robust data handling capabilities. Python’s versatility and efficiency make it well-suited for tasks such as web scraping, data preprocessing, sentiment analysis, and simulation of trading strategies.
Libraries and Tools:
Beautiful Soup: Utilized for web scraping to extract news articles from selected financial news platforms. Beautiful Soup facilitates the parsing of HTML and XML documents, enabling the extraction of relevant text data.
Pattern: Employed for text processing, including the generation of n-grams and the implementation of stemming algorithms. Pattern’s NLP capabilities streamline the transformation of textual data into analyzable units.
Pandas and NumPy: Used for data manipulation and numerical computations, facilitating efficient handling of large datasets.
Matplotlib and Seaborn: Integrated for data visualization, enabling the creation of charts and graphs to illustrate sentiment scores and stock price movements.
Workflow Overview:
Data Extraction: News articles are scraped from selected platforms using Beautiful Soup, focusing on articles published within the defined six-month period and containing relevant keywords.
Data Cleaning: The extracted text is cleaned by removing punctuation, special characters, and excessive whitespace. Duplicate articles are identified and removed to ensure data integrity.
Tokenization and N-grams Generation: The cleaned text is tokenized into unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams. Stemming is applied to standardize words to their base forms, enhancing the accuracy of sentiment matching.
Sentiment Scoring: The tokenized n-grams are compared against the sentiment dictionary. Positive and negative terms are tallied to compute sentiment scores for each article.
Decision Making: Based on the aggregated sentiment scores and predefined thresholds, buy, sell, or hold decisions are generated.
Portfolio Simulation: Trades are simulated within thirty minutes of news releases, and returns are calculated by comparing trade execution prices with the closing prices of the day.
Performance Evaluation: The accuracy of the model is assessed by comparing the predicted stock movement directions with actual market movements, thereby determining the model’s efficacy.
Model Validation and Performance Metrics
To ensure the reliability and validity of the sentiment-based prediction model, rigorous validation techniques and performance metrics are employed.
Directional Accuracy:
One of the primary metrics used to evaluate the model’s performance is directional accuracy, which measures the percentage of correct predictions regarding the direction of stock price movements (i.e., whether the price will go up or down). A higher directional accuracy indicates a more effective model in forecasting market trends based on sentiment scores.
Confusion Matrix:
A confusion matrix is constructed to provide a detailed breakdown of prediction outcomes. It categorizes predictions into true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives, offering insights into the model’s strengths and areas for improvement.
Return on Investment (ROI):
ROI is calculated to assess the profitability of the trading strategy implemented based on sentiment analysis. It measures the gains or losses generated from trades relative to the amount invested, providing a tangible metric for evaluating the model’s financial effectiveness.
Benchmark Comparison:
The model’s performance is compared against baseline benchmarks, such as a buy-and-hold strategy or random trading, to contextualize its efficacy. This comparison highlights the added value of incorporating sentiment analysis into stock prediction models.
Statistical Significance:
Statistical tests are conducted to determine the significance of the model’s predictions. This ensures that the observed performance improvements are not due to random chance but are attributable to the sentiment analysis methodology.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
Ethical Considerations:
The study adheres to ethical standards in data collection and analysis. News articles are sourced from publicly available platforms, and no proprietary or confidential information is used without authorization. Additionally, the model’s predictive capabilities are intended for informational purposes and should not be solely relied upon for making investment decisions without professional consultation.
Limitations:
While the methodology is robust, certain limitations must be acknowledged:
Sector Specificity: The sentiment dictionary is tailored to the pharmaceutical sector, limiting the model’s applicability to other industries without further customization.
Threshold Calibration: The predefined thresholds for buy, sell, and hold decisions are based on empirical observations and may require adjustment to optimize performance across different market conditions.
Market Efficiency: The model assumes that sentiment is a leading indicator of stock price movements. However, in highly efficient markets, information is rapidly incorporated into stock prices, potentially reducing the predictive power of sentiment analysis.
Data Lag: Despite the thirty-minute trading window, there may be a lag between news release and trading execution, affecting the model’s ability to capture immediate market reactions accurately.
External Factors: The model primarily focuses on news sentiment and does not account for other influential factors such as macroeconomic indicators, geopolitical events, or technological changes that can impact stock prices.
Implementation
The successful execution of the methodology outlined in this study hinges on the seamless integration of various tools, technologies, and data handling processes. This section delves into the practical aspects of implementing the sentiment analysis and stock prediction model, highlighting the programming environment, libraries utilized, and the intricate data handling procedures that ensure the robustness and accuracy of the analysis.
Tools and Technologies
Programming Language
Python was selected as the primary programming language for this study due to its versatility, extensive library ecosystem, and strong community support. Python’s ability to handle large datasets efficiently, coupled with its proficiency in data manipulation and analysis, makes it an ideal choice for implementing complex machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Additionally, Python’s readability and ease of use facilitate rapid development and iterative testing, essential for refining the sentiment analysis model.
Libraries
Several Python libraries were employed to streamline various components of the implementation process:
Beautiful Soup:
Beautiful Soup is a powerful library for web scraping and parsing HTML and XML documents. It was instrumental in extracting relevant news articles from selected financial news platforms. Beautiful Soup’s intuitive syntax and robust parsing capabilities ensured efficient data extraction, even from complex and dynamically structured web pages.Pattern:
The Pattern library was utilized for text processing tasks, including the generation of n-grams and the application of stemming algorithms. Pattern’s comprehensive suite of NLP tools facilitated the transformation of raw textual data into structured formats suitable for sentiment analysis. Its built-in functions for tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and parsing significantly reduced the complexity of text preprocessing.Pandas and NumPy:
Pandas was employed for data manipulation and analysis, providing data structures such as DataFrames that are essential for handling and organizing large datasets. NumPy complemented Pandas by offering efficient numerical operations and array handling, which are crucial for processing stock price data and performing statistical computations.Matplotlib and Seaborn:
For data visualization, Matplotlib and Seaborn were integrated to create informative and aesthetically pleasing charts and graphs. These visualizations were pivotal in illustrating sentiment scores, stock price movements, and the performance of the prediction model, thereby enhancing the interpretability of the results.Scikit-learn:
Scikit-learn was leveraged for implementing machine learning algorithms and evaluating model performance. Its comprehensive collection of tools for model training, validation, and evaluation ensured that the sentiment analysis model was both accurate and reliable.
Data Handling
Effective data handling is paramount to the integrity and success of the sentiment analysis and stock prediction model. This study meticulously addressed data collection, preprocessing, and synchronization to ensure that the analysis was both accurate and meaningful.
Scraping News Articles
Source Selection and Access:
The primary sources for news articles were reputable financial news platforms that offer comprehensive coverage of the pharmaceutical sector. Websites such as Moneycontrol.com were chosen for their reliability, extensive archives, and sector-specific news coverage. These platforms provide timely updates on regulatory decisions, corporate announcements, and market analyses that are critical for understanding sentiment trends.
Web Scraping Process:
The web scraping process was orchestrated using Beautiful Soup in Python. The following steps were undertaken to ensure effective data extraction:
URL Identification:
Relevant URLs corresponding to news sections focused on the pharmaceutical industry were identified. This included pages dedicated to regulatory news, quarterly financial results, clinical trial outcomes, and other pertinent topics.HTML Parsing:
Beautiful Soup parsed the HTML content of each identified URL, allowing for the extraction of article titles, publication dates, and full-text content. Specific HTML tags and classes associated with article content were targeted to accurately retrieve the necessary information.Data Extraction:
The scraper navigated through pagination and dynamic content loading mechanisms to collect a comprehensive dataset of news articles published over the defined six-month period. Special attention was paid to extracting only the relevant sections of each article to minimize the inclusion of extraneous information.Data Storage:
Extracted articles were stored in structured formats such as CSV files, with columns for the article title, publication date, and content. This organization facilitated subsequent preprocessing and analysis steps.
Ensuring Data Relevance and Integrity:
To maintain the relevance and integrity of the collected data, the scraper implemented several filtering criteria:
Keyword Filtering:
Articles were filtered based on the presence of specific keywords related to regulatory bodies (e.g., “FDA,” “EMA”), financial performance indicators (e.g., “Q1,” “Q2”), and other sector-specific terms. This ensured that only articles with significant implications for stock movements were included in the dataset.Deduplication:
Duplicate articles, which can arise from syndication or multiple sources reporting the same news, were identified and removed. This step was crucial to prevent skewed sentiment scores and ensure that each news piece contributed uniquely to the analysis.Time Frame Enforcement:
Only articles published within the six-month window were retained, ensuring that the dataset remained temporally relevant and aligned with recent market conditions.
Processing Stock Data
Source Selection and Access:
Stock price data was sourced from Investing.com, a reliable provider of real-time and historical financial data. Investing.com offers detailed stock information, including intraday prices, trading volumes, and historical trends, making it an ideal choice for this study.
Data Retrieval:
The retrieval of stock price data involved the following steps:
API Utilization:
Investing.com’s API was accessed to download historical stock prices for pharmaceutical companies included in the Nifty Pharma Index. The API facilitated automated and efficient data retrieval, reducing the need for manual downloads.Intraday Data Collection:
To capture short-term stock movements in response to news sentiments, intraday data with 30-minute intervals was collected. This granularity allows for the analysis of immediate market reactions following news releases.Data Formatting:
Retrieved stock price data was organized into structured formats, typically as Pandas DataFrames. Each record included the timestamp, opening price, closing price, high, low, and trading volume for each 30-minute interval.Data Cleaning:
The stock price data underwent cleaning processes to handle missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. Missing data points were imputed using appropriate statistical methods, and outliers were examined to determine if they represented genuine market movements or data errors.
Synchronization with News Data:
Aligning stock price data with news articles was essential to accurately assess the impact of sentiment on stock movements. The following steps ensured effective synchronization:
Timestamp Alignment:
Each news article was assigned a precise publication timestamp. Stock price data was then aligned to these timestamps to identify the corresponding 30-minute interval in which the news was released.Event Window Definition:
An event window was defined around each news release to capture the stock price movements immediately before and after the news. For instance, if a news article was published at 10:15 AM, the corresponding stock price intervals from 10:00 AM to 10:30 AM were considered to analyze the immediate market reaction.Data Integration:
The sentiment scores derived from news articles were merged with the synchronized stock price data. This integration facilitated the analysis of how sentiment shifts corresponded with subsequent stock price changes within the defined event windows.Handling Multiple Articles:
In cases where multiple news articles were released within a short time frame, their sentiment scores were aggregated to provide a comprehensive sentiment measure for the overlapping event windows. This approach ensured that the combined sentiment influence of simultaneous news pieces was accurately reflected in the analysis.
Workflow Overview
The implementation process followed a systematic workflow, ensuring that each step was meticulously executed to maintain data quality and analytical rigor. The workflow encompassed the following stages:
Data Extraction:
News articles were scraped from selected financial news platforms using Beautiful Soup, focusing on articles published within the six-month period and containing relevant keywords.Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
The extracted text was cleaned by removing punctuation, special characters, and excessive whitespace. Duplicate articles were eliminated, and the remaining text was tokenized into unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams. Stemming was applied to standardize word forms, enhancing the accuracy of sentiment matching.Sentiment Scoring:
The tokenized n-grams were compared against the specialized sentiment dictionary. Positive and negative terms were tallied to compute an aggregate sentiment score for each news article, providing a quantitative measure of the sentiment conveyed.Decision Making:
Based on the aggregated sentiment scores and predefined thresholds, buy, sell, or hold decisions were generated. These decisions formed the basis of the trading strategy simulated in the portfolio.Portfolio Simulation:
Trades were simulated within thirty minutes of news releases, and returns were calculated by comparing trade execution prices with the closing prices of the day. This simulation provided a tangible measure of the model’s predictive efficacy and financial performance.Performance Evaluation:
The model’s accuracy in predicting stock movement directions was assessed using directional accuracy metrics. Additional performance metrics, such as return on investment (ROI) and confusion matrix analysis, were employed to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s effectiveness.
Technical Execution
The practical execution of the methodology was facilitated by the robust and flexible tools provided by the Python programming environment. The following aspects highlight the technical execution in detail:
Automation of Data Collection:
Python scripts were developed to automate the web scraping process, ensuring timely and efficient extraction of news articles. Scheduled runs of the scraping scripts ensured that new articles were continuously gathered and integrated into the dataset, maintaining the study’s temporal relevance.Efficient Data Processing:
Leveraging Pandas and NumPy, the data was processed in-memory, allowing for rapid manipulation and transformation. This efficiency was crucial given the large volume of news articles and high-frequency stock price data involved in the analysis.Scalability and Modularity:
The implementation was designed to be scalable and modular, enabling easy adjustments to the data collection period, sentiment dictionary, and decision-making thresholds. This flexibility allows the model to be adapted for different sectors or extended to incorporate additional data sources without significant restructuring.Error Handling and Data Integrity:
Comprehensive error handling mechanisms were integrated into the scraping and data processing scripts to address potential issues such as network interruptions, unexpected HTML structures, or data inconsistencies. Logging frameworks were employed to monitor the execution process, facilitating the identification and resolution of errors promptly.Reproducibility:
To ensure that the study’s findings could be replicated and validated by other researchers, all scripts and configurations were documented meticulously. Version control systems, such as Git, were used to track changes and maintain the integrity of the implementation process.
Data Security and Compliance
Given the sensitivity of financial data, appropriate measures were taken to ensure data security and compliance with relevant regulations:
Data Anonymization:
Personally identifiable information (PII) was excluded from the news articles to protect privacy and adhere to data protection standards.Secure Storage:
All collected data was stored in secure databases with restricted access, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data confidentiality.Compliance with Terms of Service:
The web scraping activities were conducted in accordance with the terms of service of the chosen news platforms, ensuring ethical and legal compliance throughout the data collection process.
Evaluation and Results
The effectiveness of any predictive model is inherently tied to its ability to deliver accurate and reliable outcomes. In this study, the sentiment analysis model’s performance was rigorously evaluated to determine its efficacy in forecasting stock movements within the pharmaceutical sector. This section presents the key findings of the model’s predictive accuracy, illustrative case studies, underlying assumptions, the impact of threshold settings, and the inherent limitations of the approach.
Performance Metrics
Directional Accuracy
One of the primary indicators of the model’s performance is its directional accuracy, which measures the percentage of correct predictions regarding the upward or downward movement of stock prices. In this study, the sentiment analysis model achieved a 70.59% directional accuracy. This means that approximately 71 out of every 100 predictions made by the model accurately reflected the actual movement of the stock price following the release of relevant news articles.
This level of accuracy is significant, particularly in the context of financial markets where even marginal improvements in prediction accuracy can translate into substantial financial gains. The model’s ability to correctly anticipate stock price directions suggests that news sentiment is a valuable indicator for short-term stock movements in the pharmaceutical sector. Moreover, this accuracy rate positions the model favorably against traditional forecasting methods that often rely solely on quantitative data such as historical prices and trading volumes.
Case Studies
To illustrate the practical application and effectiveness of the sentiment analysis model, specific instances where the model accurately predicted buy or sell decisions based on news sentiment are examined. These case studies provide tangible evidence of the model’s capability to respond to real-world events and their impact on stock prices.
Example 1: FDA Regulatory Announcement
A notable instance occurred when a major pharmaceutical company received an unfavorable announcement from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The news article, containing negative sentiment related to regulatory observations and potential delays in drug approvals, was processed by the sentiment analysis model. The aggregated sentiment score was significantly negative, surpassing the predefined sell threshold of -0.5%. Consequently, the model generated a sell decision for the company’s stock.
Shortly after the news release, the stock price experienced a sharp decline of over 1%, validating the model’s prediction. This instance underscores the model’s proficiency in detecting negative sentiment associated with critical regulatory events and translating it into timely sell decisions to mitigate potential losses.
Example 2: Quarterly Earnings Report
Conversely, another case involved a positive quarterly earnings report from a leading pharmaceutical firm. The news article highlighted substantial revenue growth, successful drug launches, and optimistic future projections, resulting in a highly positive sentiment score well above the buy threshold of +0.5%. The model responded by generating a buy decision.
Subsequent trading within the thirty-minute window saw the stock price increase by approximately 0.7%, aligning with the model’s prediction. This example demonstrates the model’s ability to identify and act upon positive sentiments derived from favorable financial reports, thereby capitalizing on upward stock movements.
Example 3: Neutral Market Sentiment
In a third scenario, a news article reported on routine operational updates that conveyed a neutral sentiment, with no significant impact on the company’s outlook. The sentiment score fell within the hold threshold range of -0.5% to +0.5%, prompting the model to advise holding the stock.
As anticipated, the stock price remained relatively stable, showing no significant movement beyond the 1% threshold. This case highlights the model’s capability to recognize and appropriately respond to neutral sentiments, avoiding unnecessary trading actions that could incur transaction costs without yielding substantial benefits.
Assumptions
Several foundational assumptions underpin the functionality and evaluation of the sentiment analysis model. These assumptions are critical for interpreting the results and understanding the model’s operational context.
Trading Execution
A key assumption in this study is the immediate execution of trades within thirty minutes of news release. This rapid trading window is designed to capture the immediate market reaction to news sentiment before other market forces can influence stock prices. The assumption is that investors and the model act swiftly to capitalize on sentiment-driven price movements, thereby maximizing the model’s predictive utility.
However, this assumption may not fully account for real-world trading delays, such as execution times and liquidity constraints, which could affect the model’s real-time applicability and profitability.
Threshold Effectiveness
The effectiveness of the model’s decision-making is heavily influenced by the predefined sentiment thresholds for buy, sell, and hold decisions. These thresholds are set at +0.5% for buy decisions, -0.5% for sell decisions, and a range of -0.5% to +0.5% for hold decisions.
Impact on Decision Accuracy
Buy/Sell Thresholds: The +0.5% and -0.5% thresholds were chosen to ensure that only significant sentiment shifts trigger trading actions. These thresholds help filter out minor sentiment fluctuations that are unlikely to result in substantial stock movements, thereby enhancing the model’s precision and reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives.
Hold Threshold: The broader range for hold decisions accommodates sentiments that do not strongly indicate either bullish or bearish trends. This prevents overtrading and aligns with a strategy of maintaining positions when sentiment is neutral or inconclusive.
The chosen thresholds have a direct impact on the model’s accuracy by balancing sensitivity and specificity. They are calibrated to respond to meaningful sentiment changes while minimizing the influence of noise, thereby contributing to the overall directional accuracy of 70.59%.
Limitations
While the sentiment analysis model demonstrates promising results, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations to provide a balanced perspective on its applicability and performance.
Sector Specificity
The model is specifically tailored to the pharmaceutical sector, utilizing a domain-specific sentiment dictionary that captures the unique language and sentiment drivers within this industry. While this specialization enhances the model’s accuracy within the pharmaceutical sector, it limits its generalizability to other sectors without significant modifications. Different industries may have distinct sentiment indicators and regulatory environments, necessitating the development of new sentiment dictionaries and potentially different threshold settings for accurate predictions.
Market Forces
The evaluation of the model controlled for broader market movements by focusing on individual stock performances rather than overall market indices. While this isolation helps in assessing the model’s effectiveness in a controlled environment, it does not account for external market forces that can influence stock prices independently of news sentiment. Factors such as macroeconomic trends, geopolitical events, and market-wide investor sentiment can impact stock movements, potentially confounding the model’s predictions. Future studies could incorporate these broader market variables to enhance the model’s robustness and applicability in more complex market scenarios.
Additional Limitations
Data Lag and Execution Delays: The assumption of immediate trading within thirty minutes may not hold in real-world trading environments where execution delays can occur, potentially reducing the model’s effectiveness.
Sentiment Dictionary Completeness: Although the sentiment dictionary is tailored to the pharmaceutical sector, it may not encompass all relevant terms or capture the full complexity of sentiment expressed in news articles, leading to potential gaps in sentiment scoring.
Dynamic Market Conditions: The model’s performance is evaluated within a specific six-month period. Market conditions are inherently dynamic, and the model’s accuracy may fluctuate under different market regimes or during periods of heightened volatility.
Discussion
The results of this study underscore the promising potential of sentiment analysis as a robust tool for predicting stock market movements within the pharmaceutical sector. Achieving a directional accuracy of 70.59% highlights the efficacy of leveraging news sentiment in financial forecasting, positioning sentiment-based models as valuable complements to traditional prediction methods.
Model Efficacy
The notable accuracy of the sentiment-based model can be attributed to several key factors. Firstly, the domain-specific sentiment dictionary played a crucial role in accurately capturing the nuanced language and sentiment expressions unique to the pharmaceutical industry. By focusing on terms and phrases that directly impact investor perceptions within this sector, the model effectively translated qualitative news sentiments into quantitative indicators. Additionally, the integration of n-gram analysis — encompassing unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams — enhanced the model’s ability to understand context and sentiment nuances, thereby improving prediction precision. The strategic choice of 30-minute interval stock data further enabled the model to respond swiftly to sentiment shifts, capturing immediate market reactions post-news release.
Sector-Specific Insights
Tailoring the sentiment dictionary to the pharmaceutical sector was instrumental in achieving high accuracy. The pharmaceutical industry is uniquely sensitive to regulatory announcements, clinical trial outcomes, and global health events, all of which significantly influence investor sentiment and stock performance. A customized sentiment lexicon ensured that the model could accurately interpret the sentiment conveyed in industry-specific news, such as FDA approvals or drug recalls. This sector-specific approach mitigates the risk of misclassification that might occur with generic sentiment dictionaries, thereby enhancing the model’s relevance and reliability in predicting stock movements within this field.
Comparison with Traditional Methods
When contrasted with conventional technical and fundamental analysis, the sentiment-based approach offers distinct advantages. Traditional methods primarily rely on historical price data, trading volumes, and financial indicators to forecast stock movements. While these quantitative techniques provide valuable insights, they often overlook the qualitative aspects of market behavior driven by investor sentiment and news events. In contrast, the sentiment-based model incorporates qualitative data from news articles, capturing real-time investor emotions and reactions that can precede actual market movements. This integration of sentiment analysis provides a more holistic view of the market, potentially identifying trends and shifts that traditional methods might miss. Consequently, combining sentiment-based models with traditional analyses can lead to more comprehensive and accurate forecasting strategies.
Practical Implications
The practical implications of this study are significant for both investors and financial analysts. By incorporating sentiment analysis into their decision-making processes, investors can gain an additional layer of insight into market trends, enhancing their ability to make informed trading decisions. For instance, a positive sentiment score derived from favorable news can prompt investors to buy stocks, anticipating price increases, while negative sentiments can signal sell decisions to avoid potential losses. Financial analysts can also utilize sentiment-based models to augment their reports and recommendations, providing clients with a more nuanced understanding of market dynamics.
Moreover, the model’s relatively high accuracy suggests that sentiment analysis can serve as a valuable predictive tool in volatile sectors like pharmaceuticals, where news events can rapidly influence stock prices. By integrating such models into their analytical frameworks, investors and analysts can better navigate the complexities of the stock market, leveraging both quantitative data and qualitative sentiment indicators to optimize their investment strategies.